


Embarking on a low-carb diet can be a transformative journey toward better health and weight management. However, navigating the world of food choices can be daunting. To help you stay on track and make informed decisions, here are 10 foods to avoid while following a low-carb diet:

Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that is naturally present in many foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. It is also added to various processed foods and beverages during manufacturing to enhance flavor. While sugar provides a quick source of energy for the body, excessive consumption of sugary foods can have negative effects on health.
Sugary foods, such as candies, pastries, sodas, and sweetened snacks, are high in added sugars. These added sugars contribute to the calorie content of these foods without providing essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, or fiber. Consuming too much added sugar can lead to weight gain, tooth decay, and an increased risk of chronic health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
It’s important to be mindful of your sugar intake and make healthier choices when it comes to sugary foods. Opting for whole fruits instead of sugary snacks, choosing water or unsweetened beverages over sugary drinks, and reading food labels to identify added sugars can help you maintain a balanced diet and reduce the negative impact of sugar on your health.
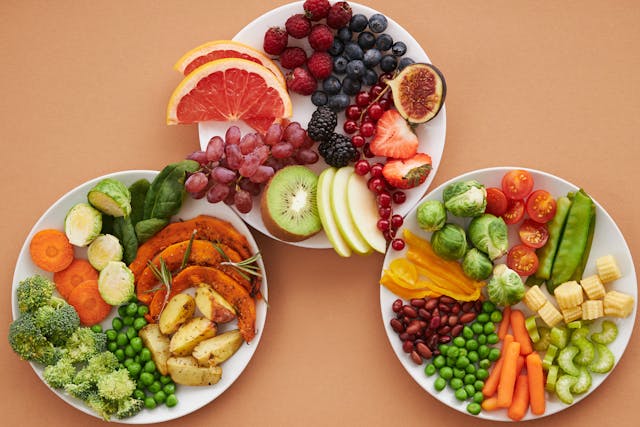
Starchy vegetables are a type of vegetable that contains a higher amount of carbohydrates compared to non-starchy vegetables. They are rich in nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them a valuable part of a healthy diet. Examples of starchy vegetables include potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, peas, and winter squash.
These vegetables are an excellent source of complex carbohydrates, which are digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates found in sugary foods. This slow digestion helps regulate blood sugar levels and provides a steady release of energy. Starchy vegetables also contain fiber, which supports digestive health, promotes satiety, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Despite their nutritional benefits, it’s essential to consume starchy vegetables in moderation, especially for individuals managing conditions like diabetes or trying to lose weight. Balancing starchy vegetables with non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help create a well-rounded and nutritious diet.
High-sugar fruits are those that contain a relatively large amount of natural sugars compared to other fruits. While all fruits contain natural sugars such as fructose and glucose, some varieties are notably higher in sugar content. These fruits can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet but may need to be consumed in moderation, especially for individuals who are watching their sugar intake or managing conditions like diabetes.
Some examples of high-sugar fruits include:
While high-sugar fruits offer various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they can contribute to spikes in blood sugar levels if consumed excessively. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes or those monitoring their sugar intake to be mindful of portion sizes when consuming high-sugar fruits.
Additionally, incorporating a variety of fruits into your diet, including lower-sugar options like berries, citrus fruits, and apples, can provide a well-rounded nutrient profile while managing overall sugar intake. Balancing high-sugar fruits with vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can contribute to a balanced and healthy diet.
Sugary beverages are typically high in carbohydrates, particularly in the form of added sugars like sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup. For individuals following a low-carb diet, such as the ketogenic diet or a general low-carbohydrate approach, sugary beverages are generally avoided or limited due to their potential to spike blood sugar levels and hinder ketosis (the metabolic state where the body burns fat for fuel).
Examples of sugary beverages that are high in carbohydrates include:
For those on a low-carb diet, opting for sugar-free or low-carb alternatives to these beverages can be a better choice. Some options include:
Overall, being mindful of your beverage choices and opting for low-carb or sugar-free options can support your goals on a low-carbohydrate diet.
Sweetened condiments and sauces are flavorful additions to meals but can also contribute a significant amount of added sugars to your diet. These condiments and sauces are typically infused with sugars, syrups, or sweeteners to enhance taste, but they can also increase calorie intake and impact overall health if consumed excessively.
Common examples of sweetened condiments and sauces include:
While these condiments and sauces can add delicious flavors to dishes, they are often high in added sugars, which can contribute to health issues like weight gain, insulin resistance, and dental problems if consumed in excess.
For individuals looking to reduce their sugar intake, opting for alternatives to sweetened condiments and sauces can be beneficial. Some options include:
By being mindful of your consumption of sweetened condiments and sauces and exploring healthier alternatives, you can enjoy flavorful meals while reducing your intake of added sugars and promoting overall well-being.
High-carb snacks are food items that contain a significant amount of carbohydrates, which are the body’s primary source of energy. While carbohydrates are essential for providing fuel, especially for physical activity, it’s important to choose high-carb snacks wisely to maintain a balanced diet. Here are some examples of high-carb snacks:
When choosing high-carb snacks, it’s essential to consider the quality of carbohydrates. Opt for whole grain options, fruits, vegetables, and snacks that also provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Balancing high-carb snacks with protein, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods can help regulate blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and support overall health and well-being.
Many low-fat or diet products replace fat with added sugars and artificial ingredients. Read labels carefully and opt for natural, full-fat alternatives like Greek yogurt, cheese, and unsweetened nut butters.
Alcoholic beverages can be high in carbs and calories, especially cocktails, beer, and sweetened wines. If you choose to drink, opt for dry wines, spirits like vodka or whiskey with zero-carb mixers, or light beers in moderation.
Processed snacks like chips, crackers, and packaged meals often contain hidden carbs, sugars, and unhealthy fats. Choose whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible to support your low-carb lifestyle.
Say goodbye to bread, pasta, rice, and cereals made from grains. These are rich in carbohydrates that can spike blood sugar levels. Explore low-carb alternatives like cauliflower rice, zucchini noodles, or almond flour-based bread.
LowCarb Avenue offers low carb breads that are suitable for individuals following low-carb or ketogenic diets. The bread options are designed to be lower in carbohydrates compared to traditional bread while still providing a satisfying texture and taste. Here are some key aspects of low carb avenue’s bread:
Overall, lowcarbavenue.com bread provides a convenient and tasty option for individuals looking to reduce their carbohydrate intake without sacrificing the enjoyment of bread-based foods.
By steering clear of these high-carb foods and making smart substitutions, you can stay on course with your low-carb diet and enjoy a wide variety of delicious and nutritious options. Remember, a balanced approach and mindful eating are key to long-term success and well-being.



















Sign up below to receive exclusive deals and be first to know when delicious new products are coming out.